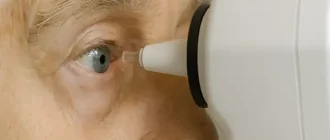
Have you ever wondered why your vision sometimes feels off, even after you’ve just visited the optometrist? Astigmatism could be the culprit, but what exactly is astigmatism, and how does it affect your vision?
Prevalence of Astigmatism by Age Group
| Age Group | Percentage of Cases |
|---|---|
| Children (0-12) | 25% |
| Teens (13-19) | 30% |
| Adults (20-40) | 35% |
| Older Adults (40+) | 40% |
This chart shows the prevalence of astigmatism across different age groups, illustrating an increase in cases with age.
What Is Astigmatism?
Astigmatism is a common refractive error that occurs when the cornea or lens inside the eye has an irregular shape. In a perfect world, your cornea would be evenly curved like a basketball. In the world of astigmatism, however, it looks more like a football. This uneven shape causes light to be focused improperly on the retina, leading to blurred or distorted vision.
Factors Influencing the Onset or Development of Astigmatism
| Factor | Influence on Astigmatism Development |
|---|---|
| Genetics | High |
| Eye Injury or Surgery | Moderate |
| Keratoconus | Very High |
| Frequent Eye Strain | Moderate |
| Eye Development During Childhood | High |
This chart displays the various factors that can influence the onset or progression of astigmatism, ranging from genetics to eye strain.
Astigmatism can be present from birth or develop later in life, and it often coexists with nearsightedness (myopia) or farsightedness (hyperopia). It doesn’t mean there’s something drastically wrong with your eyes; it simply means they aren’t quite as symmetrically shaped as they could be.
How Does Astigmatism Affect Your Daily Vision?
Blurred vision is the most common symptom of astigmatism, but it’s not just a matter of seeing everything out of focus. The condition can lead to eyestrain, headaches, and even double vision. Imagine trying to read a book, and every other letter looks like it has a shadow. Not exactly a recipe for a relaxing afternoon, right?
Effects of Astigmatism on Visual Acuity at Different Distances
| Distance | Quality of Vision with Astigmatism |
|---|---|
| Near (Reading) | Blurred or shadowed letters |
| Mid (Computer Work) | Eyestrain and fatigue |
| Far (Driving) | Blurred vision with halos |
This chart shows the effects of astigmatism on visual acuity at different distances, from near tasks like reading to far distances like driving.
You might also notice that nighttime driving becomes a nightmare—astigmatism can cause halos and glare around lights, making it particularly challenging to see in low-light conditions. Streetlights, oncoming headlights, and traffic signals suddenly develop a glowing aura, which might sound mystical but is actually pretty dangerous.
Impact of Astigmatism on Vision Quality
| Activity | Effect of Astigmatism |
|---|---|
| Reading | Blurred or shadowed text |
| Nighttime Driving | Increased glare and halos |
| Computer Work | Eyestrain and headaches |
This chart illustrates the different effects of astigmatism on daily activities, such as reading, driving at night, and working on a computer.
Did You Know?
Astigmatism affects about one in three Americans, according to the American Optometric Association. You’re certainly not alone if you’ve been prescribed those cylindrical correction lenses! (Source: American Optometric Association)
Types of Astigmatism
Astigmatism isn’t one-size-fits-all; there are two main types: corneal and lenticular. Corneal astigmatism occurs when the cornea itself is misshaped, whereas lenticular astigmatism arises from irregularities in the shape of the lens.
Corneal vs. Lenticular Astigmatism
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Corneal Astigmatism | Uneven curvature of the cornea, the front surface of the eye. |
| Lenticular Astigmatism | Irregular shape of the lens inside the eye. |
Understanding the type of astigmatism helps in determining the best treatment option, whether it’s corrective lenses or other interventions.
Can Astigmatism Get Worse Over Time?
The big question—does it get worse? The answer isn’t straightforward. Astigmatism can change over time, especially during childhood when the eye is still developing. Factors such as genetics or eye injuries can also influence its progression.
Astigmatism is usually stable by adulthood, but certain conditions like keratoconus, where the cornea becomes thinner and more conical, can worsen astigmatism. If you notice any sudden changes in your vision, it’s best to see an eye specialist right away.
Did You Know?
Laser eye surgery, such as LASIK, can correct astigmatism in many cases, often resulting in 20/20 vision. But it’s not for everyone—severe cases may require other corrective measures. (Source: Mayo Clinic)
How Is Astigmatism Diagnosed?
Astigmatism is typically diagnosed during a routine eye exam using a device called a phoropter. Your optometrist might also use a keratometer, which measures the curvature of your cornea. It’s a pretty straightforward process—there’s no need to fear any poking or prodding.
Treatments: More Than Just Glasses
While glasses and contact lenses are the most common treatments, there are other options available. LASIK and PRK are popular laser surgery methods that reshape the cornea, reducing or even eliminating astigmatism in many cases.
Comparison of Treatment Options
| Treatment Option | Effectiveness | Cost (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Glasses | Highly effective for mild to moderate astigmatism | $100 – $300 |
| Contact Lenses | Effective, with toric lenses designed specifically for astigmatism | $150 – $400 annually |
| Laser Surgery (LASIK/PRK) | Permanent solution, but not suitable for all patients | $2,000 – $4,000 per eye |
Astigmatism Correction Methods – Popularity by Percentage
| Correction Method | Popularity (%) |
|---|---|
| Glasses | 60% |
| Contact Lenses | 30% |
| Laser Surgery | 10% |
This chart highlights the popularity of different astigmatism correction methods, with glasses being the most commonly chosen option.
Lifestyle Changes for Managing Astigmatism
While lifestyle changes can’t cure astigmatism, reducing eyestrain can certainly help you manage the symptoms. Remember the 20-20-20 rule: every 20 minutes, take a 20-second break and look at something 20 feet away. And yes, this means you have a legitimate reason to stare out of the window at work—tell your boss it’s doctor’s orders.
It’s also essential to have proper lighting when reading or working on a computer. Straining your eyes in dim light or sitting too close to your screen can make astigmatism symptoms more noticeable.
Our Editorial Advice
If you think you might have astigmatism, the best course of action is to schedule an eye exam. Blurred vision might seem like a minor inconvenience, but it can affect everything from driving safety to the way you perceive the world around you. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can make a significant difference in your quality of life.
Remember, astigmatism is common and manageable. Whether you choose glasses, contacts, or surgery, there are effective ways to improve your vision and reduce discomfort. Keep an eye on your health—literally!