Ophthalmologist and Eye Diseases
An ophthalmologist (eye doctor) is a doctor who specializes in the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of eye disease. It is difficult to overestimate the severity of vision problems - a large part of the surrounding world ceases to exist for a person. Treating and preventing private and total loss of vision is what an ophthalmologist does.
Subsections of ophthalmology
Pediatric ophthalmology is a subsection of ophthalmology that investigates the characteristics of children's vision. A child's vision, unlike that of an adult, is constantly changing. Pediatric ophthalmology is designed to study the peculiarities of these changes and related pathologies.
What organs do ophthalmologists treat
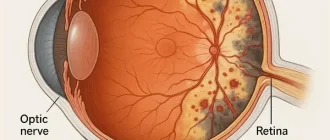
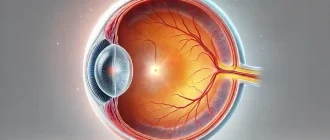
- The eyeball;
- eyelids;
- lacrimal organs;
- conjunctiva;
- orbit.
What diseases are treated by an ophthalmologist
- nearsightedness is a visual defect in which the image is focused in front of the retina and the person cannot see distant objects clearly;
- farsightedness is a visual defect in which the image is focused behind the retina and a person cannot see objects clearly at close range;
- conjunctivitis - inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye (conjunctiva);
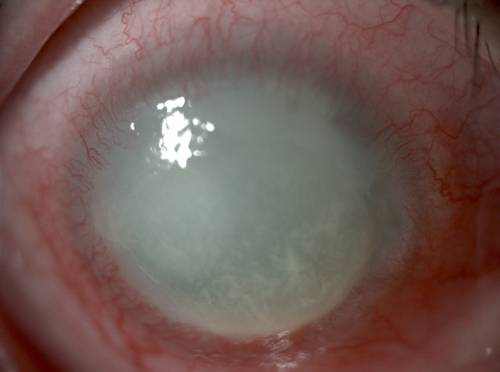
- cataract - clouding of the lens of the eye;
- glaucoma - increased eye pressure that causes visual impairment;
- astigmatism - a disturbance in the shape of the lens or cornea.
What else does an ophthalmologist treat?
A large part of what an ophthalmologist treats are vision abnormalities that are triggered by other diseases or critical situations for the body. Visual impairment can be caused by:
- hypertension;
- abnormal pregnancy;
- severe childbirth;
- atherosclerosis;
- renal pathologies;
- diabetes mellitus;
- traumatic eye injuries.
How is the examination by an ophthalmologist?
At the initial reception, the ophthalmologist:
- Gathers anamnesis (medical history), asks the patient about possible complaints.
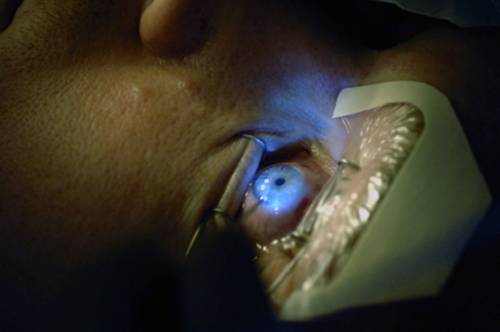
- Conducts examination and palpation (palpation) of the eyes, examination of the eyes with a biomicroscope (slit lamp).
- Depending on complaints and examination results, the doctor may prescribe additional tests: ophthalmoscopy (visual examination of the eye fundus), tonometry (measuring intraocular pressure), and biomicroscopy (examination of the eye under multiple magnification).
Modern ophthalmic clinics rarely question whether imaging of the anterior segment is necessary. The
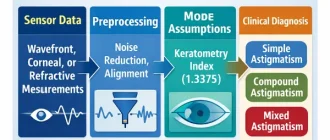
When clinicians talk about mixed astigmatism, it is usually framed as a refractive condition
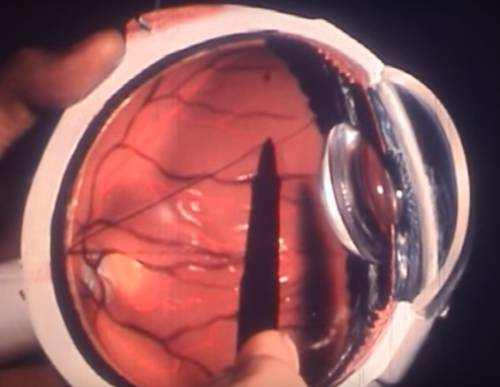
Modern cataract surgery no longer tolerates biometric uncertainty that was acceptable twenty years ago.
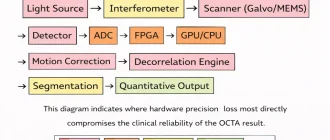
Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography (OCTA) is commonly presented as a dye‑free method for visualizing
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) systems rarely lose image quality suddenly. In most cases, degradation
Excimer laser systems used for corneal refractive surgery are 193 nm ultraviolet pulsed ablation
When clinicians talk about severe vision loss or total blindness, the discussion often stays
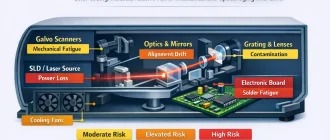
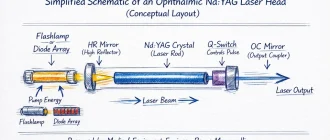
Ophthalmic Nd:YAG Lasers as a Clinical Platform I approach ophthalmic Nd:YAG laser systems as
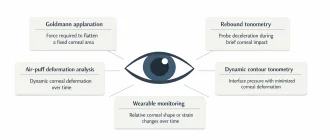
From an engineering standpoint, intraocular pressure (IOP) is not a directly accessible variable. There
Thermal pulsation systems have become a widely used technical solution for treating evaporative dry
Eye drops for photophobia are commonly used to reduce light sensitivity, a condition where
Aphakia is a condition in which the eye’s natural lens is completely absent, leaving
Ocular migraine is a temporary visual disturbance that can cause flashes of light, blind
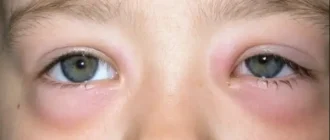
Swollen or puffy eyes in babies occur when fluid builds up around the delicate
Sometimes that pain over left eye feels like a small storm building right behind
Polycoria — an eye anomaly that makes even ophthalmologists pause for a second look.
Exotropia, often referred to as “wall-eyes,” is a form of strabismus where one or
When your eyes start to feel dry, itchy, or irritated, choosing the right drops
The 2025 update in glaucoma management is rewriting the rulebook. With artificial intelligence reshaping
If you’ve ever found yourself stretching your arm farther and farther just to read
A sudden bright-red patch on the white of your eye can be startling. It
Have you ever noticed a sudden black spot in your vision? Or perhaps zigzagging
Phlyctenulosis may sound like the name of an obscure ancient city, but in reality,
CMV retinitis is a serious viral infection of the retina caused by the cytomegalovirus
Blurry vision in the morning might seem like one of those “wake-up quirks,” but
Corneal neovascularization (CNV) is a condition where new, abnormal blood vessels invade the cornea
With approximately 12 million Americans over the age of 40 living with vision impairment,
Myopia, commonly known as short-sightedness, is a visual condition where close objects appear clear,
Think of ocular myasthenia gravis (OMG) as a glitch in your body’s electrical wiring
Most people don’t think about their eye health—until those little changes in vision start
Gas permeable (GP) contact lenses—also known as RGP or hard lenses—are rigid lenses that
Optic neuritis is a sudden inflammation of the optic nerve, the critical cable that
Uveitis is an inflammation of the uvea, the middle layer of the eye located
Warts on the eyelids? Yeah, not fun. These pesky growths can be uncomfortable, a
Itchy eyelid swelling isn’t just about puffiness or discomfort—it’s your body’s way of sounding
Ocular tonometry is a diagnostic procedure used to measure the intraocular pressure (IOP) inside
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) and bioflavonoids are often dubbed the “power couple” of eye
Fuchs’ corneal dystrophy is a progressive eye disease that affects the innermost layer of
Progressive lenses are multifocal eyeglass lenses designed to correct presbyopia—age-related difficulty focusing on close
A macular hole is a small break in the macula—the central part of the
Our eyes endure daily strain from screens, environmental factors, and aging. Proper nutrition plays
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun is more than just a threat to your
Presbyopia is an age-related vision condition that makes it difficult to focus on close
If you’re thinking about switching to contact lenses or just curious about the process,
The use of contact lenses for children has evolved significantly in recent years. Once
The world of vision correction is evolving, and multifocal supplementary lenses are at the
Narrow-angle glaucoma (also called angle-closure glaucoma) is a serious eye condition where the drainage
Orthokeratology (Ortho-K) is a non-surgical method for correcting vision using specially designed gas-permeable contact
Have you noticed that reading small text on your phone or a restaurant menu
Ocular rosacea is a chronic inflammatory condition that affects the eyes, often in conjunction
When selecting eyeglass lenses, understanding the differences between polycarbonate and Trivex materials is essential
Dry eyes are a common and often temporary side effect following LASIK surgery. While
If your eyes feel unusually painful after removing your contact lenses, you might dismiss
“Legally blind” is a term used primarily for legal and governmental purposes to determine
Choosing the right eyeglass lenses is crucial for optimizing your vision and ensuring comfort
Bloodshot eyes in children can be alarming for any parent. Understanding the root cause
Drooping eyelid, or ptosis, is a condition where the upper eyelid sags over the
LASIK (Laser-Assisted In Situ Keratomileusis) surgery is one of the most popular refractive surgeries
Contact lenses are a popular and convenient alternative to glasses, offering clear vision without
Can Contact Lenses Cause Fungal Eye Infections? Yes, they can. While contact lenses are