Pupils that are dilated, referred to also as mydriasis, refer to the enlargement of the pupil, the dark center of the eyes. This growth permits more light into the retina, and it is a crucial aspect of how our sight adapts to dimly lit conditions.
The dilation and constriction of pupils are reflex reactions controlled by our autonomic nervous system. A balance between two muscles – sphincter pupillae (constricts pupil) and dilator pupillae (dilates pupil) – regulate this action. The purpose is primarily vision-centric: dilation in dim light for enhanced visibility and constriction to prevent excessive light intake in brightly lit environments.
On the other hand, consistently enlarged pupils may suggest potential health dangers like a severe head injury or the use of specific drugs. If you notice prolonged pupil dilation without any clear cause, it is always advisable to seek advice from a healthcare expert.
Causes of Dilated Pupils
Pupil dilation can occur for various reasons. Not all are cause for concern, but some might warrant prompt medical attention.
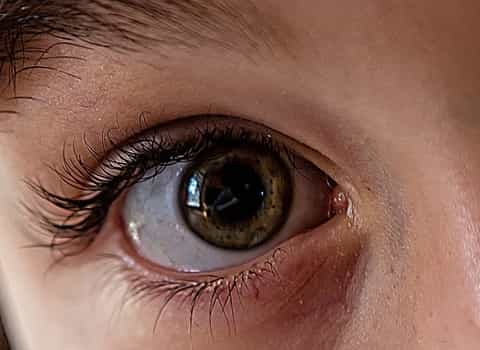
1. Low Lighting Conditions
Your eyes may open wider in dark environments in order to let in more light for clearer sight.
2. Medications and Drugs
Certain medications may have dilating pupils as an unwanted effect. Taking recreational drugs may also cause the eyes to widen abnormally.
3. Emotional State and Excitement
When someone is feeling strong emotions or is very excited, the diameter of their pupils can increase.
4. Brain Injury or Trauma
Head injuries can result in dilated pupils by disrupting normal brain function.
5. Medical Conditions
Medical conditions like glaucoma, brain tumors, or stroke may lead to dilated pupils.
Dangers of Dilated Pupils
1. Increased Sensitivity to Light
When your pupils are enlarged, more light is let in to the eyes. This could lead to elevated sensitivity to light, causing distress or even agony in extreme cases.
2. Impaired Vision and Focus
Dilated pupils might lead to blurry vision due to an imbalance of light and focus. This can impair the capability to see details clearly, particularly during reading or driving.
3. Eye Strain and Fatigue
Struggling to focus with dilated pupils can cause strain on your eyes, leading to fatigue and headaches.
4. Increased Risk of Eye Infections
Dilated pupils can expose more of the eye’s surface, potentially amplifying the risk of infections and eye injuries.
5. Underlying Health Issues
Prolonged or frequent dilation may point to underlying health issues, like nerve disorders, drug use, or certain eye diseases. If you have unexplained, persistent dilation of your pupils, it’s important to seek medical attention promptly.
Dilated pupils do not always signify danger, but awareness of these potential dangers can help guide your response to this symptom.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Signs that dilated pupils may require medical attention:
Shared Symptoms: If dilated pupils are accompanied by other unusual symptoms like sensitivity to light, blurred vision, or headaches, these could be signs of a more serious condition requiring immediate medical attention.
Duration: Dilated pupils that last for an extended period even after the stimulus (bright light) has been removed may signal a need for closer examination by a healthcare professional.
Sudden Change: Abrupt change in pupil size without any apparent triggers could be an indication of a significant health problem.
Remember, informing your doctor about the recent history of symptoms can assist in diagnosing the cause faster and accurately.



