Therapy of amblyopia and also strabismus might include glasses, spots, exercises and potentially even surgery. Early treatment is clearly extra efficient, nevertheless, we have usually achieved success in therapy of both amblyopia as well as strabismus in later years.
Amblyopia
The brain as well as the eyes collaborate to generate vision. The eye focuses light on the back component of the eye known as the retina. Cells of the retina then set off nerve signals that follow the optic nerves to the mind. Amblyopia is the clinical term used when the vision of one eye is reduced due to the fact that it cannot work effectively with the brain. The eye itself looks normal, but also for various factors the brain favors the other eye. This condition is also occasionally called lazy eye.

Amblyopia is one of the most usual cause of aesthetic problems among children, affecting around 2 to 3 from every 100 children. Unless it is efficiently dealt with in very early childhood, amblyopia normally persists right into the adult years. It is also the most usual reason for monocular (one eye) visual impairment among young and also middle-aged adults.
Causes
Amblyopia can result from any condition that prevents the eye from focusing clearly. Amblyopia can be triggered by the imbalance of both eyes – a problem called strabismus. With strabismus, the eyes could cross in (esotropia) or turn out (exotropia). Sometimes, amblyopia is caused by a clouding of the front part of the eye, a problem called cataract.
An usual root cause of amblyopia is the failure of one eye to concentrate in addition to the various other one. Amblyopia can occur when one eye is much more nearsighted, more farsighted, or has more astigmatism. These terms describe the capability of the eye to focus light on the retina. Farsightedness, or hyperopia, takes place when the range from the front to the rear of the eye is also short. Eyes that are farsighted have the tendency to focus much better at a distance but have much more trouble concentrating on near things. Nearsightedness, or nearsightedness, takes place when the eye is also long from front to back. Eyes with nearsightedness have the tendency to focus better on near things. Eyes with astigmatism have trouble concentrating on far and near things because of their irregular form.
Strabismus
Strabismus is any kind of imbalance of the eyes. It is estimated that 4% of the United States population has strabismus.
What are the types of strabismus and how are they called? There are several types of strabismus. Strabismus is most commonly explained by the instructions of the eye imbalance; common types of strabismus are esotropia, exotropia, hypotropia, and also hypertropia.
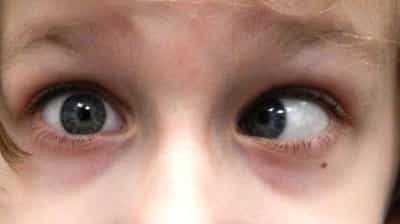
Strabismus could also be defined by its cause. The 3 cranial nerves (III, IV, VI) in charge of eye activity could be weak or palsied and cause strabismus. Some instances of paralytic strabismus consist of third nerve palsy and exceptional oblique palsy.
Special patterns of strabismus could have distinct names such as Brown syndrome, and also Duane syndrome.
Causes
The majority of strabismus is the outcome of a problem of the badly recognized neuromuscular (including mind) control of eye motion. Much less frequently, a problem with the real eye muscle mass causes strabismus.



